How to Use Annotations in go-doudou Applications
We all know that Go language doesn't have native annotations, but when developing business applications, the lack of annotations can make front-end and back-end coordination difficult. go-doudou has implemented support for annotations through Go's standard library ast/parser.
Quick Start
We'll demonstrate the usage and effects through a simple service developed with go-doudou.
Preparation
- Install the latest version of go-doudou CLI locally
go install -v github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2@v2.0.8
Install Postman locally for testing APIs: https://www.postman.com/
Install GoLand locally
Initialize the Project
Our service name and module name are both called annotation
go-doudou svc init annotation
Design Business Interface
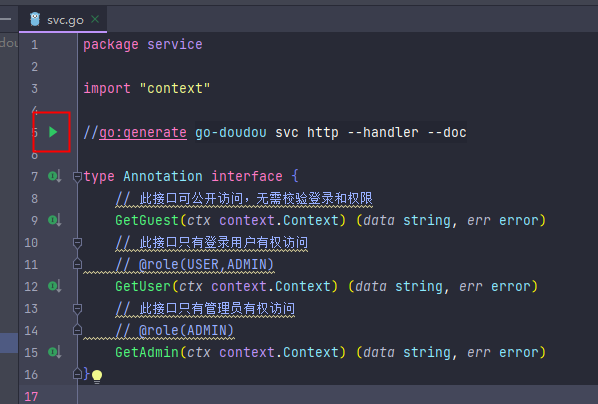
The interface definition file for go-doudou applications is the svc.go file in the project root path. Open the file and modify it as follows:
package service
import "context"
//go:generate go-doudou svc http --handler --doc
type Annotation interface {
// This interface is publicly accessible, no login or permission validation needed
GetGuest(ctx context.Context) (data string, err error)
// This interface is only accessible to logged-in users
// @role(USER,ADMIN)
GetUser(ctx context.Context) (data string, err error)
// This interface is only accessible to administrators
// @role(ADMIN)
GetAdmin(ctx context.Context) (data string, err error)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
@role(USER,ADMIN) and @role(ADMIN) are the focus of this article. The annotation definition format is: @annotationName(param1,param2,param3...). You can customize various annotations according to your business requirements. @role is just an example; you can also define others like @permission(create,update,del), and parameter-less annotations like @inner().
Generate Code
Click the green triangle in the upper left corner of the screenshot to execute the go:generate instruction, which will generate interface routes and HTTP handler related code, as well as JSON documentation following the OpenAPI 3.0 specification.
Let's focus on the transport/httpsrv/handler.go file.
/**
* Generated by go-doudou v2.0.8.
* Don't edit!
*/
package httpsrv
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/framework"
"github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/framework/rest"
)
type AnnotationHandler interface {
GetGuest(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)
GetUser(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)
GetAdmin(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)
}
func Routes(handler AnnotationHandler) []rest.Route {
return []rest.Route{
{
Name: "GetGuest",
Method: "GET",
Pattern: "/guest",
HandlerFunc: handler.GetGuest,
},
{
Name: "GetUser",
Method: "GET",
Pattern: "/user",
HandlerFunc: handler.GetUser,
},
{
Name: "GetAdmin",
Method: "GET",
Pattern: "/admin",
HandlerFunc: handler.GetAdmin,
},
}
}
// Store the parsed annotation information in memory
// framework.AnnotationStore is an alias for map[string][]Annotation type,
// where the key is the route name, and the value is a slice of annotation structures.
// The annotation structure stores the annotation name and parameter slice.
// The principle of the permission validation middleware we implement below is to get the route name from the http.Request object,
// then use the route name to find the stored annotation structure slice from RouteAnnotationStore,
// and finally compare the user roles obtained from the in-memory data source or external data source
// with the elements in the parameter slice of the annotation structure
// to determine whether the user has permission to continue accessing the interface
var RouteAnnotationStore = framework.AnnotationStore{
"GetUser": {
{
Name: "@role",
Params: []string{
"USER",
"ADMIN",
},
},
},
"GetAdmin": {
{
Name: "@role",
Params: []string{
"ADMIN",
},
},
},
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
Download Dependencies
Execute the go mod tidy command to download project dependencies. At this point, the service can be started, but let's not rush. Next, we'll write middleware based on the annotation information to implement our requirement to control access permissions based on user roles.
Auth Middleware
The login credential for this sample project uses a base64 token for HTTP basic authentication. Let's open the transport/httpsrv/middleware.go file and paste the following code:
/**
* Generated by go-doudou v2.0.8.
* You can edit it as your need.
*/
package httpsrv
import (
"annotation/vo"
"github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/framework/rest/httprouter"
"github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/toolkit/sliceutils"
"net/http"
)
// vo.UserStore is an alias type for map[Auth]RoleEnum, where the key is a structure composed of username and password, and the value is a role enumeration
// We use userStore to represent the database
func Auth(userStore vo.UserStore) func(inner http.Handler) http.Handler {
return func(inner http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Get the route name from http.Request
paramsFromCtx := httprouter.ParamsFromContext(r.Context())
routeName := paramsFromCtx.MatchedRouteName()
// Check if the route has associated annotation structure slices
// If not, allow the request to proceed
if !RouteAnnotationStore.HasAnnotation(routeName, "@role") {
inner.ServeHTTP(w, r)
return
}
// Extract and parse HTTP basic username and password from the request header
user, pass, ok := r.BasicAuth()
// If not successful, deny access, return 401
if !ok {
w.Header().Set("WWW-Authenticate", `Basic realm="Provide user name and password"`)
w.WriteHeader(401)
w.Write([]byte("Unauthorised.\n"))
return
}
// Check if this user exists in userStore
role, exists := userStore[vo.Auth{user, pass}]
// If it doesn't exist, deny access, return 401
if !exists {
w.Header().Set("WWW-Authenticate", `Basic realm="Provide user name and password"`)
w.WriteHeader(401)
w.Write([]byte("Unauthorised.\n"))
return
}
// If it exists, check if the interface allows access to users of that role
params := RouteAnnotationStore.GetParams(routeName, "@role")
// Check if the parameter slice of the @role annotation for this route includes the user's role
// If not, deny access, return 403
if !sliceutils.StringContains(params, role.StringGetter()) {
w.WriteHeader(403)
w.Write([]byte("Access denied\n"))
return
}
// If it includes the user's role, allow access
inner.ServeHTTP(w, r)
})
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
Define Enums
Next, we need to define an enumeration for roles. Create a vo directory in the project root directory, and create a new vo.go file inside, pasting the following code:
package vo
type Auth struct {
User string
Pass string
}
// RoleEnum is a type alias for int
type RoleEnum int
// Define enum constants
const (
GUEST RoleEnum = iota
USER
ADMIN
)
// StringSetter conversion from string to enum constants
func (r *RoleEnum) StringSetter(value string) {
switch value {
case "GUEST":
*r = GUEST
case "USER":
*r = USER
case "ADMIN":
*r = ADMIN
default:
*r = GUEST
}
}
// StringGetter conversion from enum constants to string
func (r *RoleEnum) StringGetter() string {
switch *r {
case GUEST:
return "GUEST"
case USER:
return "USER"
case ADMIN:
return "ADMIN"
default:
return "GUEST"
}
}
// UserStore is an alias type for map[Auth]RoleEnum, simulating a database
type UserStore map[Auth]RoleEnum
// Define some users
func NewUserStore() UserStore {
return UserStore{
Auth{
User: "admin",
Pass: "admin",
}: ADMIN,
Auth{
User: "usr1",
Pass: "usr1",
}: USER,
Auth{
User: "usr2",
Pass: "usr2",
}: USER,
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
Implement the Interface
Open the transport/httpsrv/annotationhandlerimpl.go file, pasting the following code:
/**
* Generated by go-doudou v2.0.8.
* You can edit it as your need.
*/
package httpsrv
import (
"annotation/service"
"github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/framework/rest"
"net/http"
)
type AnnotationHandlerImpl struct {
service.Annotation
}
func (receiver *AnnotationHandlerImpl) GetGuest(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
result, err := receiver.Annotation.GetGuest(r.Context())
if err != nil {
rest.ErrorResp(w, r, err)
return
}
rest.SuccessResp(w, r, result)
}
func (receiver *AnnotationHandlerImpl) GetUser(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
result, err := receiver.Annotation.GetUser(r.Context())
if err != nil {
rest.ErrorResp(w, r, err)
return
}
rest.SuccessResp(w, r, result)
}
func (receiver *AnnotationHandlerImpl) GetAdmin(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
result, err := receiver.Annotation.GetAdmin(r.Context())
if err != nil {
rest.ErrorResp(w, r, err)
return
}
rest.SuccessResp(w, r, result)
}
func NewAnnotationHandler(annotation service.Annotation) AnnotationHandler {
return &AnnotationHandlerImpl{
annotation,
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
Open the svcimpl/svcimpl.go file, pasting the following code:
/**
* Generated by go-doudou v2.0.8.
* You can edit it as your need.
*/
package svcimpl
import (
"annotation/service"
"context"
)
type AnnotationImpl struct {
}
func (receiver *AnnotationImpl) GetGuest(_ context.Context) (data string, err error) {
return "GetGuest from service layer", nil
}
func (receiver *AnnotationImpl) GetUser(_ context.Context) (data string, err error) {
return "GetUser from service layer", nil
}
func (receiver *AnnotationImpl) GetAdmin(_ context.Context) (data string, err error) {
return "GetAdmin from service layer", nil
}
func NewAnnotation() service.Annotation {
return &AnnotationImpl{}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
Finally, open the cmd/main.go file, pasting the following code:
/**
* Generated by go-doudou v2.0.8.
* You can edit it as your need.
*/
package main
import (
"annotation/svcimpl"
"annotation/transport/httpsrv"
"annotation/vo"
"context"
"github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/framework/configutils"
v3 "github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/framework/rest"
"github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/toolkit/zlogger"
"os"
"os/signal"
"syscall"
"time"
)
func main() {
defer func() {
if err := recover(); err != nil {
zlogger.Error(err)
}
}()
var (
conf v3.HttpServerConfig
server *v3.HttpServer
)
configutils.SetConfigName("config")
conf = v3.HttpServerConfig{
Host: configutils.GetString("GDD_HOST", "localhost"),
Port: configutils.GetInt("GDD_PORT", 6060),
Mode: configutils.GetString("GDD_MODE", "release"),
PayloadCodec: configutils.GetString("GDD_PAYLOAD_CODEC", "json"),
ReadTimeout: configutils.GetInt("GDD_READ_TIMEOUT", 10),
WriteTimeout: configutils.GetInt("GDD_WRITE_TIMEOUT", 10),
IdleTimeout: configutils.GetInt("GDD_IDLE_TIMEOUT", 90),
MaxRequestBodySize: configutils.GetInt("GDD_MAX_REQUEST_BODY_SIZE", 2),
LoggerOptions: nil,
SwaggerOptions: nil,
RouteNotFoundHandler: nil,
DebugErrorStackOptions: nil,
SetAuthOptions: nil,
HealthyCheckOptions: nil,
PageOptions: nil,
CriteriaOptions: nil,
SortOptions: nil,
ReqLoggerOptions: nil,
PrintRoutesOptions: nil,
SerRespOkStatusCodeAs: nil,
SerRespFailStatusCodeAs: nil,
EnableCors: configutils.GetBool("GDD_ENABLE_CORS", true),
TlsCertFile: configutils.GetString("GDD_TLS_CERT_FILE", ""),
TlsKeyFile: configutils.GetString("GDD_TLS_KEY_FILE", ""),
InsecureSkipVerify: configutils.GetBool("GDD_INSECURE_SKIP_VERIFY", false),
DisableGlobalWsCors: configutils.GetBool("GDD_DISABLE_GLOBAL_WS_CORS", false),
RequestMatcher: nil,
}
service := svcimpl.NewAnnotation()
handler := httpsrv.NewAnnotationHandler(service)
server = v3.NewHttpServer(conf)
server.AddMiddleware(httpsrv.Auth(vo.NewUserStore()))
routes := httpsrv.Routes(handler)
server.AddRoutes(routes)
go func() {
if err := server.Run(); err != nil {
zlogger.Error(err)
}
}()
quit := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(quit, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM)
<-quit
zlogger.Info("Shutdown Server ...")
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 3*time.Second)
defer cancel()
if err := server.Shutdown(ctx); err != nil {
zlogger.Error("Server Shutdown:", err)
}
zlogger.Info("Server exiting")
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
Start the Service
Execute the go run cmd/main.go command to start the service.
Test with Postman
First test the
/guestendpoint:- Create a new request in Postman, set the method to
GET - Set the URL to
http://localhost:6060/guest - Send the request, you should receive a response with data: "GetGuest from service layer"
- Create a new request in Postman, set the method to
Then test the
/userendpoint:- Create a new request in Postman, set the method to
GET - Set the URL to
http://localhost:6060/user - In the "Auth" tab, select "Basic Auth"
- Enter username:
usr1, password:usr1 - Send the request, you should receive a response with data: "GetUser from service layer"
- Create a new request in Postman, set the method to
Finally test the
/adminendpoint:- Create a new request in Postman, set the method to
GET - Set the URL to
http://localhost:6060/admin - In the "Auth" tab, select "Basic Auth"
- Enter username:
admin, password:admin - Send the request, you should receive a response with data: "GetAdmin from service layer"
- Create a new request in Postman, set the method to
Try to test the
/adminendpoint with a user role account:- Create a new request in Postman, set the method to
GET - Set the URL to
http://localhost:6060/admin - In the "Auth" tab, select "Basic Auth"
- Enter username:
usr1, password:usr1 - Send the request, you should receive a 403 forbidden response with the message: "Access denied"
- Create a new request in Postman, set the method to
Conclusion
Through this example, we've demonstrated how to use annotations in go-doudou applications to implement role-based access control. The key points are:
- Define the annotation in the comments of interface methods in the
svc.gofile - The annotation will be parsed and stored in the
RouteAnnotationStoreby go-doudou's code generator - Implement a middleware that uses the annotation to perform the necessary logic, in this case, checking if the user has the required role to access a specific API
- Apply the middleware in the main function
The same approach can be used for other custom annotations that suit your business needs.