gRPC
Service Registration and Discovery
go-doudou supports two service registration and discovery mechanisms: etcd and nacos. REST services registered in the registry will automatically have the _rest suffix added to their service name, and gRPC services will have the _grpc suffix, to distinguish between them.
Tip
The etcd and nacos mechanisms can be used simultaneously in one service
GDD_SERVICE_DISCOVERY_MODE=etcd,nacos
Etcd
go-doudou has built-in support for using etcd as a registry center for service registration and discovery since v2. The following environment variables need to be configured:
GDD_SERVICE_NAME: Service name, requiredGDD_SERVICE_DISCOVERY_MODE: Service registration and discovery mechanism name,etcd, requiredGDD_ETCD_ENDPOINTS: etcd connection address, required
GDD_SERVICE_NAME=grpcdemo-server
GDD_SERVICE_DISCOVERY_MODE=etcd
GDD_ETCD_ENDPOINTS=localhost:2379
2
3
Nacos
go-doudou has built-in support for using Alibaba's Nacos as a registry center for service registration and discovery. The following environment variables need to be configured:
GDD_SERVICE_NAME: Service name, requiredGDD_NACOS_SERVER_ADDR: Nacos server address, requiredGDD_SERVICE_DISCOVERY_MODE: Service discovery mechanism name, required
GDD_SERVICE_NAME=test-svc # Required
GDD_NACOS_SERVER_ADDR=http://localhost:8848/nacos # Required
GDD_SERVICE_DISCOVERY_MODE=nacos # Required
2
3
Zookeeper
go-doudou has built-in support for using Zookeeper as a registry center for service registration and discovery. The following environment variables need to be configured:
GDD_SERVICE_NAME: Service name, requiredGDD_SERVICE_DISCOVERY_MODE: Service discovery mechanism name, requiredGDD_ZK_SERVERS: Zookeeper server address, required
GDD_SERVICE_NAME=cloud.unionj.ServiceB # Required
GDD_SERVICE_DISCOVERY_MODE=zk # Required
GDD_ZK_SERVERS=localhost:2181 # Required
GDD_ZK_DIRECTORY_PATTERN=/dubbo/%s/providers
GDD_SERVICE_GROUP=group
GDD_SERVICE_VERSION=v2.2.2
2
3
4
5
6
Client-side Load Balancing
Simple Round Robin Load Balancing (For Etcd)
You need to call etcd.NewRRGrpcClientConn("service name registered in etcd", tlsOption) to create a *grpc.ClientConn instance.
func main() {
// Need to close the etcd client before the program exits
defer etcd.CloseEtcdClient()
conf := config.LoadFromEnv()
tlsOption := grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials())
// Create a gRPC connection that supports etcd simple round robin load balancing mechanism
grpcConn := etcd.NewRRGrpcClientConn("grpcdemo-server_grpc", tlsOption)
// Need to close the gRPC connection before the program exits
defer grpcConn.Close()
svc := service.NewEnumDemo(conf, pb.NewHelloworldServiceClient(grpcConn),
client.NewHelloworldClient(ddclient.WithClient(newClient()), ddclient.WithProvider(restProvider)))
handler := httpsrv.NewEnumDemoHandler(svc)
srv := rest.NewRestServer()
srv.AddRoute(httpsrv.Routes(handler)...)
srv.Run()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Smooth Weighted Round Robin Load Balancing (For Etcd)
You need to call etcd.NewSWRRGrpcClientConn("service name registered in etcd", tlsOption) to create a *grpc.ClientConn instance.
func main() {
// Need to close the etcd client before the program exits
defer etcd.CloseEtcdClient()
conf := config.LoadFromEnv()
tlsOption := grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials())
// Create a gRPC connection that supports etcd smooth weighted round robin load balancing mechanism (SWRR)
grpcConn := etcd.NewSWRRGrpcClientConn("grpcdemo-server_grpc", tlsOption)
// Need to close the gRPC connection before the program exits
defer grpcConn.Close()
svc := service.NewEnumDemo(conf, pb.NewHelloworldServiceClient(grpcConn))
handler := httpsrv.NewEnumDemoHandler(svc)
srv := rest.NewRestServer()
srv.AddRoute(httpsrv.Routes(handler)...)
srv.Run()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Simple Round Robin Load Balancing (For Nacos)
Call the nacos.NewRRGrpcClientConn method to create a gRPC connection.
func main() {
// Need to close the nacos client before the program exits
defer nacos.CloseNamingClient()
conf := config.LoadFromEnv()
tlsOption := grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials())
// Create a gRPC connection that supports nacos simple round robin load balancing mechanism
grpcConn := nacos.NewRRGrpcClientConn(nacos.NacosConfig{
ServiceName: "grpcdemo-server_grpc",
}, tlsOption)
// Need to close the gRPC connection before the program exits
defer grpcConn.Close()
svc := service.NewEnumDemo(conf, pb.NewHelloworldServiceClient(grpcConn))
handler := httpsrv.NewEnumDemoHandler(svc)
srv := rest.NewRestServer()
srv.AddRoute(httpsrv.Routes(handler)...)
srv.Run()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Weighted Round Robin Load Balancing (For Nacos)
Call the nacos.NewWRRGrpcClientConn method to create a gRPC connection.
func main() {
// Need to close the nacos client before the program exits
defer nacos.CloseNamingClient()
conf := config.LoadFromEnv()
tlsOption := grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials())
// Create a gRPC connection that supports nacos weighted round robin load balancing mechanism
grpcConn := nacos.NewWRRGrpcClientConn(nacos.NacosConfig{
ServiceName: "grpcdemo-server_grpc",
}, tlsOption)
// Need to close the gRPC connection before the program exits
defer grpcConn.Close()
svc := service.NewEnumDemo(conf, pb.NewHelloworldServiceClient(grpcConn))
handler := httpsrv.NewEnumDemoHandler(svc)
srv := rest.NewRestServer()
srv.AddRoute(httpsrv.Routes(handler)...)
srv.Run()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Simple Round Robin Load Balancing (For Zookeeper)
Call the zk.NewRRGrpcClientConn method to create a gRPC connection.
func main() {
...
tlsOption := grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials())
opts := []grpc_retry.CallOption{
grpc_retry.WithBackoff(grpc_retry.BackoffLinear(100 * time.Millisecond)),
grpc_retry.WithCodes(codes.NotFound, codes.Aborted),
}
dialOptions := []grpc.DialOption{
tlsOption,
grpc.WithStreamInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainStreamClient(
grpc_opentracing.StreamClientInterceptor(),
grpc_retry.StreamClientInterceptor(opts...),
)),
grpc.WithUnaryInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainUnaryClient(
grpc_opentracing.UnaryClientInterceptor(),
grpc_retry.UnaryClientInterceptor(opts...),
)),
}
// Set up a connection to the server.
grpcConn := zk.NewRRGrpcClientConn(zk.ServiceConfig{
Name: "cloud.unionj.ServiceB_grpc",
Group: "",
Version: "",
}, dialOptions...)
defer grpcConn.Close()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
Weighted Round Robin Load Balancing (For Zookeeper)
Call the zk.NewSWRRGrpcClientConn method to create a gRPC connection.
func main() {
...
tlsOption := grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials())
opts := []grpc_retry.CallOption{
grpc_retry.WithBackoff(grpc_retry.BackoffLinear(100 * time.Millisecond)),
grpc_retry.WithCodes(codes.NotFound, codes.Aborted),
}
dialOptions := []grpc.DialOption{
tlsOption,
grpc.WithStreamInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainStreamClient(
grpc_opentracing.StreamClientInterceptor(),
grpc_retry.StreamClientInterceptor(opts...),
)),
grpc.WithUnaryInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainUnaryClient(
grpc_opentracing.UnaryClientInterceptor(),
grpc_retry.UnaryClientInterceptor(opts...),
)),
}
// Set up a connection to the server.
grpcConn := zk.NewSWRRGrpcClientConn(zk.ServiceConfig{
Name: "cloud.unionj.ServiceB_grpc",
Group: "",
Version: "",
}, dialOptions...)
defer grpcConn.Close()
svc := service.NewServiceA(conf, bClient, pb.NewServiceBServiceClient(grpcConn))
...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
Authentication and Authorization
go-doudou has built-in interceptors grpcx_auth.UnaryServerInterceptor and grpcx_auth.StreamServerInterceptor for login authorization in the framework/grpcx/interceptors/grpcx_auth package, as well as the grpcx_auth.Authorizer interface. Developers can implement their own grpcx_auth.Authorizer interface. Below is a usage example:
Interface Definition
Note the @role annotation above the interface method definition. For go-doudou annotation usage, please refer to the relevant section in the official documentation: "Guide->Interface Definition->Annotations->Usage in gRPC Services".
package service
import "context"
//go:generate go-doudou svc http
//go:generate go-doudou svc grpc
type Annotation interface {
// This interface is publicly accessible, no need to check login and permissions
GetGuest(ctx context.Context) (data string, err error)
// This interface is only accessible to logged-in users
// @role(USER,ADMIN)
GetUser(ctx context.Context) (data string, err error)
// This interface is only accessible to administrators
// @role(ADMIN)
GetAdmin(ctx context.Context) (data string, err error)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
grpcx_auth.Authorizer Interface Implementation
Below is an example of a custom grpcx_auth.Authorizer interface implementation based on HTTP basic authentication:
package grpc
import (
"annotation/vo"
"context"
"encoding/base64"
grpc_auth "github.com/grpc-ecosystem/go-grpc-middleware/auth"
"github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/framework/grpcx/interceptors/grpcx_auth"
"github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/toolkit/sliceutils"
"strings"
"google.golang.org/grpc/codes"
"google.golang.org/grpc/status"
)
// Ensure that AuthInterceptor struct implements grpcx_auth.Authorizer interface
var _ grpcx_auth.Authorizer = (*AuthInterceptor)(nil)
// AuthInterceptor is an implementation of the grpcx_auth.Authorizer interface
type AuthInterceptor struct {
// For simplicity, we use an in-memory data structure to simulate a database user role table,
// but in a real project, you would typically define a database connection instance as a member variable,
// using a real database to query user tables, role tables, permission tables, etc.
userStore vo.UserStore
}
// NewAuthInterceptor is a factory method to create an AuthInterceptor struct instance
func NewAuthInterceptor(userStore vo.UserStore) *AuthInterceptor {
return &AuthInterceptor{
userStore: userStore,
}
}
// Parse HTTP basic token, return username and password
func parseToken(token string) (username, password string, ok bool) {
c, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(token)
if err != nil {
return "", "", false
}
cs := string(c)
username, password, ok = strings.Cut(cs, ":")
if !ok {
return "", "", false
}
return username, password, true
}
// Authorize method implements the grpcx_auth.Authorizer interface
func (interceptor *AuthInterceptor) Authorize(ctx context.Context, fullMethod string) (context.Context, error) {
method := fullMethod[strings.LastIndex(fullMethod, "/")+1:]
// For go-doudou annotation usage, please refer to the "Guide->Interface Definition->Annotations->Usage in gRPC Services" section in the official documentation
// If the gRPC method definition does not have the @role annotation, it means it can be publicly accessed without authentication, so let it pass directly
if !MethodAnnotationStore.HasAnnotation(method, "@role") {
return ctx, nil
}
// This depends on the auth package from the third-party open-source library github.com/grpc-ecosystem/go-grpc-middleware
// Extract the HTTP basic token from metadata
token, err := grpc_auth.AuthFromMD(ctx, "Basic")
if err != nil {
return ctx, err
}
// Parse the HTTP basic token, returning username and password
user, pass, ok := parseToken(token)
if !ok {
return ctx, status.Error(codes.Unauthenticated, "Provide user name and password")
}
// Find the role of the user through username and password
role, exists := interceptor.userStore[vo.Auth{user, pass}]
if !exists {
return ctx, status.Error(codes.Unauthenticated, "Provide user name and password")
}
// Get the list of roles that can access the gRPC method from MethodAnnotationStore
params := MethodAnnotationStore.GetParams(method, "@role")
// Check if the user's role is included in the role list, if it is, the authentication passes, if not, access is denied
if !sliceutils.StringContains(params, role.StringGetter()) {
return ctx, status.Error(codes.PermissionDenied, "Access denied")
}
return ctx, nil
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
Main Function
func main() {
conf := config.LoadFromEnv()
svc := service.NewAnnotation(conf)
// In-memory data structure simulating a database user role table
userStore := vo.UserStore{
vo.Auth{
User: "guest",
Pass: "guest",
}: vo.GUEST,
vo.Auth{
User: "user",
Pass: "user",
}: vo.USER,
vo.Auth{
User: "admin",
Pass: "admin",
}: vo.ADMIN,
}
// Create a custom implementation of the grpcx_auth.Authorizer interface
authorizer := pb.NewAuthInterceptor(userStore)
grpcServer := grpcx.NewGrpcServer(
grpc.StreamInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainStreamServer(
grpc_ctxtags.StreamServerInterceptor(),
grpc_opentracing.StreamServerInterceptor(),
grpc_prometheus.StreamServerInterceptor,
logging.StreamServerInterceptor(grpczerolog.InterceptorLogger(zlogger.Logger)),
// Pass the authorizer to the grpcx_auth interceptor
grpcx_auth.StreamServerInterceptor(authorizer),
grpc_recovery.StreamServerInterceptor(),
)),
grpc.UnaryInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainUnaryServer(
grpc_ctxtags.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
grpc_opentracing.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
grpc_prometheus.UnaryServerInterceptor,
logging.UnaryServerInterceptor(grpczerolog.InterceptorLogger(zlogger.Logger)),
// Pass the authorizer to the grpcx_auth interceptor
grpcx_auth.UnaryServerInterceptor(authorizer),
grpc_recovery.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
)),
)
pb.RegisterAnnotationServiceServer(grpcServer, svc)
grpcServer.Run()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
Rate Limiting
Usage
go-doudou has built-in memory rate limiters based on the token bucket algorithm implemented with golang.org/x/time/rate.
In the github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/framework/ratelimit/memrate package, there is a MemoryStore struct that stores key and Limiter instance pairs. The Limiter instance is a rate limiter instance, and the key is the key for that rate limiter instance.
You can pass an optional function memrate.WithTimer to the memrate.NewLimiter factory function to set a callback function for when the key's idle time exceeds timeout, for example, to delete the key from the MemoryStore instance to free up memory resources.
go-doudou also provides a redis rate limiter based on the GCRA rate limiting algorithm wrapped with the go-redis/redis_rate library. This rate limiter supports cross-instance global rate limiting.
Memory Rate Limiter Example
The memory rate limiter is based on local memory and only supports local rate limiting. First, you need to call memrate.NewMemoryStore to create a MemoryStore instance, which stores the keys to be limited and their corresponding rate limiters. Then call grpcx_ratelimit.NewRateLimitInterceptor(grpcx_ratelimit.WithMemoryStore(mstore)) to create a grpcx_ratelimit.RateLimitInterceptor interceptor instance. Then you need to customize a structure that implements the grpcx_ratelimit.KeyGetter interface to implement the logic of extracting keys from context.Context. Finally, add the code rl.UnaryServerInterceptor(keyGetter), to the interceptor chain to implement rate limiting. Below is an example of rate limiting client IPs.
func main() {
defer etcd.CloseEtcdClient()
conf := config.LoadFromEnv()
svc := service.NewHelloworld(conf)
go func() {
mstore := memrate.NewMemoryStore(func(_ context.Context, store *memrate.MemoryStore, key string) ratelimit.Limiter {
// Rate limiter creation function, which creates a rate limiter that allows processing 10 requests per second, with a peak of 30 requests, and a maximum idle time of 10 seconds. After being idle for more than 10 seconds, it will be removed from memory to free up memory space.
// The idle time should be at least greater than 1 / rate * burst to be meaningful, which means it should at least wait until the token bucket is refilled to its initial state.
return memrate.NewLimiter(10, 30, memrate.WithTimer(10*time.Second, func() {
store.DeleteKey(key)
}))
})
rl := grpcx_ratelimit.NewRateLimitInterceptor(grpcx_ratelimit.WithMemoryStore(mstore))
keyGetter := &RateLimitKeyGetter{}
grpcServer := grpcx.NewGrpcServer(
grpc.StreamInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainStreamServer(
// In this example, the grpc_ctxtags interceptor must be added, which automatically adds the RPC caller's "peer.address" information to the context.Context
grpc_ctxtags.StreamServerInterceptor(),
grpc_opentracing.StreamServerInterceptor(),
grpc_prometheus.StreamServerInterceptor,
logging.StreamServerInterceptor(grpczerolog.InterceptorLogger(zlogger.Logger)),
rl.StreamServerInterceptor(keyGetter),
grpc_recovery.StreamServerInterceptor(),
)),
grpc.UnaryInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainUnaryServer(
// In this example, the grpc_ctxtags interceptor must be added, which automatically adds the RPC caller's "peer.address" information to the context.Context
grpc_ctxtags.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
grpc_opentracing.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
grpc_prometheus.UnaryServerInterceptor,
logging.UnaryServerInterceptor(grpczerolog.InterceptorLogger(zlogger.Logger)),
rl.UnaryServerInterceptor(keyGetter),
grpc_recovery.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
)),
)
pb.RegisterHelloworldServiceServer(grpcServer, svc)
grpcServer.Run()
}()
handler := httpsrv.NewHelloworldHandler(svc)
srv := rest.NewRestServer()
srv.AddRoute(httpsrv.Routes(handler)...)
srv.Run()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
Custom implementation of the grpcx_ratelimit.KeyGetter interface:
var _ grpcx_ratelimit.KeyGetter = (*RateLimitKeyGetter)(nil)
type RateLimitKeyGetter struct {
}
func (r *RateLimitKeyGetter) GetKey(ctx context.Context, _ string) string {
var peerAddr string
if value, ok := grpc_ctxtags.Extract(ctx).Values()["peer.address"]; ok {
peerAddr = value.(string)
}
if stringutils.IsEmpty(peerAddr) {
if value, ok := peer.FromContext(ctx); ok {
peerAddr = value.Addr.String()
}
}
return peerAddr[:strings.LastIndex(peerAddr, ":")]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Redis Rate Limiter Example
Redis rate limiters can be used in scenarios where multiple instances need to rate limit a key at the same time. The key's expiration time equals the time required to generate 1 token based on the rate.
func main() {
defer etcd.CloseEtcdClient()
conf := config.LoadFromEnv()
svc := service.NewHelloworld(conf)
go func() {
rdb := redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{
Addr: "localhost:6379",
})
fn := redisrate.LimitFn(func(ctx context.Context) ratelimit.Limit {
// Rate limiter creation function, which creates a rate limiter that allows processing 10 requests per second, with a peak of 30 requests.
return ratelimit.PerSecondBurst(10, 30)
})
rl := grpcx_ratelimit.NewRateLimitInterceptor(grpcx_ratelimit.WithRedisStore(rdb, fn))
keyGetter := &RateLimitKeyGetter{}
grpcServer := grpcx.NewGrpcServer(
grpc.StreamInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainStreamServer(
// In this example, the grpc_ctxtags interceptor must be added, which automatically adds the RPC caller's "peer.address" information to the context.Context
grpc_ctxtags.StreamServerInterceptor(),
grpc_opentracing.StreamServerInterceptor(),
grpc_prometheus.StreamServerInterceptor,
logging.StreamServerInterceptor(grpczerolog.InterceptorLogger(zlogger.Logger)),
rl.StreamServerInterceptor(keyGetter),
grpc_recovery.StreamServerInterceptor(),
)),
grpc.UnaryInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainUnaryServer(
// In this example, the grpc_ctxtags interceptor must be added, which automatically adds the RPC caller's "peer.address" information to the context.Context
grpc_ctxtags.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
grpc_opentracing.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
grpc_prometheus.UnaryServerInterceptor,
logging.UnaryServerInterceptor(grpczerolog.InterceptorLogger(zlogger.Logger)),
rl.UnaryServerInterceptor(keyGetter),
grpc_recovery.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
)),
)
pb.RegisterHelloworldServiceServer(grpcServer, svc)
grpcServer.Run()
}()
handler := httpsrv.NewHelloworldHandler(svc)
srv := rest.NewRestServer()
srv.AddRoute(httpsrv.Routes(handler)...)
srv.Run()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
For a custom implementation of the grpcx_ratelimit.KeyGetter interface, please refer to the memory rate limiter example above.
Retry
To implement the retry mechanism, you need to depend on the retry module of the third-party open-source library github.com/grpc-ecosystem/go-grpc-middleware. Add the retry interceptor to the dialOptions slice, and then pass dialOptions as a parameter to the load balancing client factory function to create a gRPC client connection instance. For specific usage, please refer to the comments in the source code: https://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/go-grpc-middleware/blob/master/retry.
tlsOption := grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials())
opts := []grpc_retry.CallOption{
grpc_retry.WithBackoff(grpc_retry.BackoffLinear(100 * time.Millisecond)),
grpc_retry.WithCodes(codes.NotFound, codes.Aborted),
}
dialOptions := []grpc.DialOption{
tlsOption,
grpc.WithStreamInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainStreamClient(
grpc_retry.StreamClientInterceptor(opts...),
)),
grpc.WithUnaryInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainUnaryClient(
grpc_retry.UnaryClientInterceptor(opts...),
)),
}
grpcConn := nacos.NewWRRGrpcClientConn(nacos.NacosConfig{
ServiceName: "grpcdemo-server_grpc",
}, dialOptions...)
defer grpcConn.Close()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Logging
Usage
go-doudou has a global zerolog.Logger built into the github.com/unionj-cloud/go-doudou/v2/toolkit/zlogger package. If the GDD_ENV environment variable is not equal to an empty string and dev, it will include some metadata about the service itself.
You can also call the InitEntry function to customize the zerolog.Logger instance.
You can also set the log level by configuring the GDD_LOG_LEVEL environment variable, and set whether the log format is json or text by configuring the GDD_LOG_FORMAT environment variable.
You can enable HTTP request and response log printing by configuring GDD_LOG_REQ_ENABLE=true. The default is false, which means no printing.
Example
// You can use the lumberjack library to add log rotation functionality to your service
zlogger.SetOutput(io.MultiWriter(os.Stdout, &lumberjack.Logger{
Filename: filepath.Join(os.Getenv("LOG_PATH"), fmt.Sprintf("%s.log", "usersvc")),
MaxSize: 5, // Single log file maximum size is 5M, exceeding this will create a new log file
MaxBackups: 10, // Keep a maximum of 10 log files
MaxAge: 7, // Log files are kept for a maximum of 7 days
Compress: true, // Whether to enable log compression
}))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
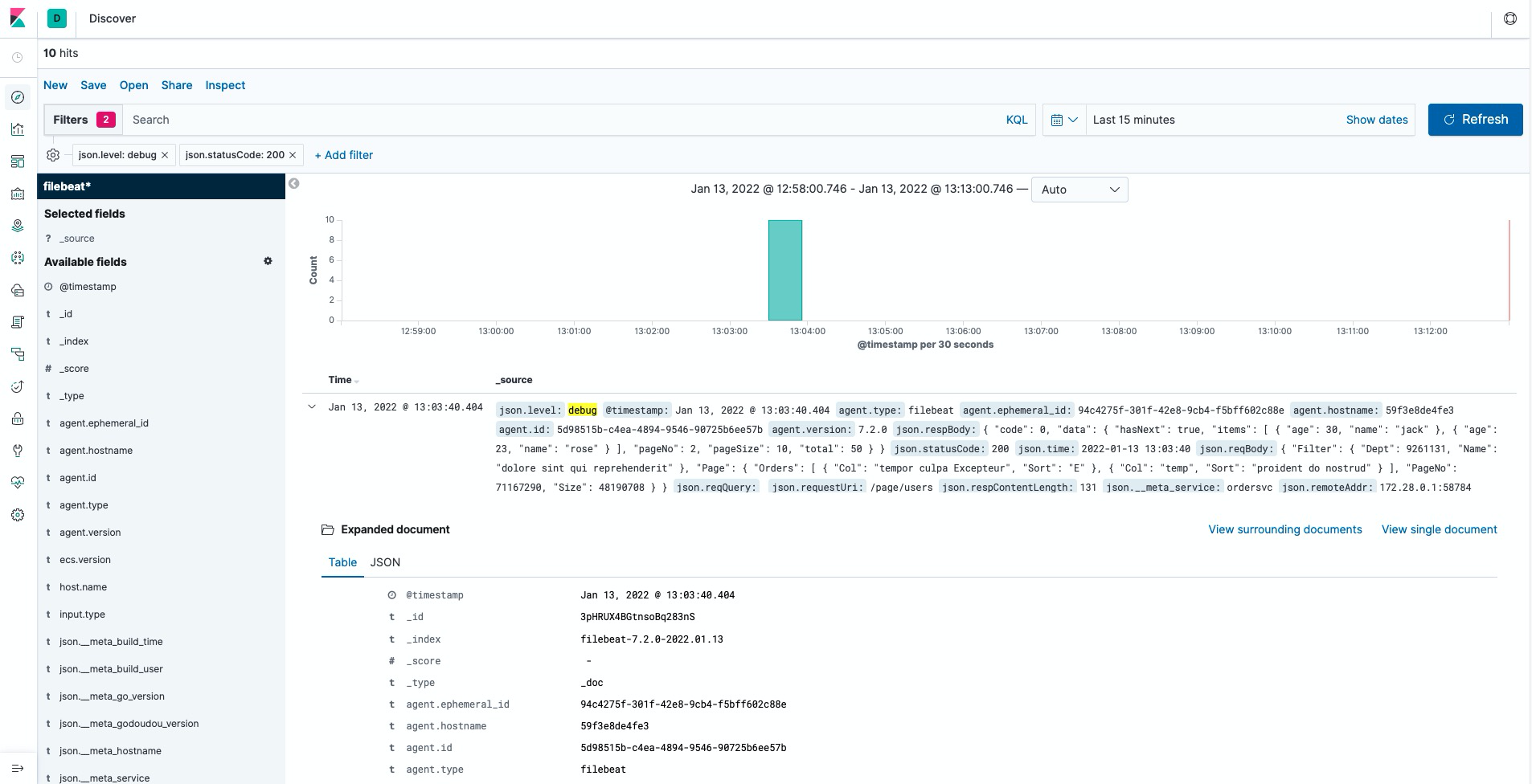
ELK Stack
The logger package supports integration with the ELK stack.
Example
version: '3.9'
services:
elasticsearch:
container_name: elasticsearch
image: "docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.2.0"
environment:
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms1g -Xmx1g"
- "discovery.type=single-node"
ports:
- "9200:9200"
volumes:
- ./esdata:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
networks:
testing_net:
ipv4_address: 172.28.1.9
kibana:
container_name: kibana
image: "docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.2.0"
ports:
- "5601:5601"
networks:
testing_net:
ipv4_address: 172.28.1.10
filebeat:
container_name: filebeat
image: "docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:7.2.0"
volumes:
- ./filebeat.yml:/usr/share/filebeat/filebeat.yml:ro
- ./log:/var/log
networks:
testing_net:
ipv4_address: 172.28.1.11
networks:
testing_net:
ipam:
driver: default
config:
- subnet: 172.28.0.0/16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
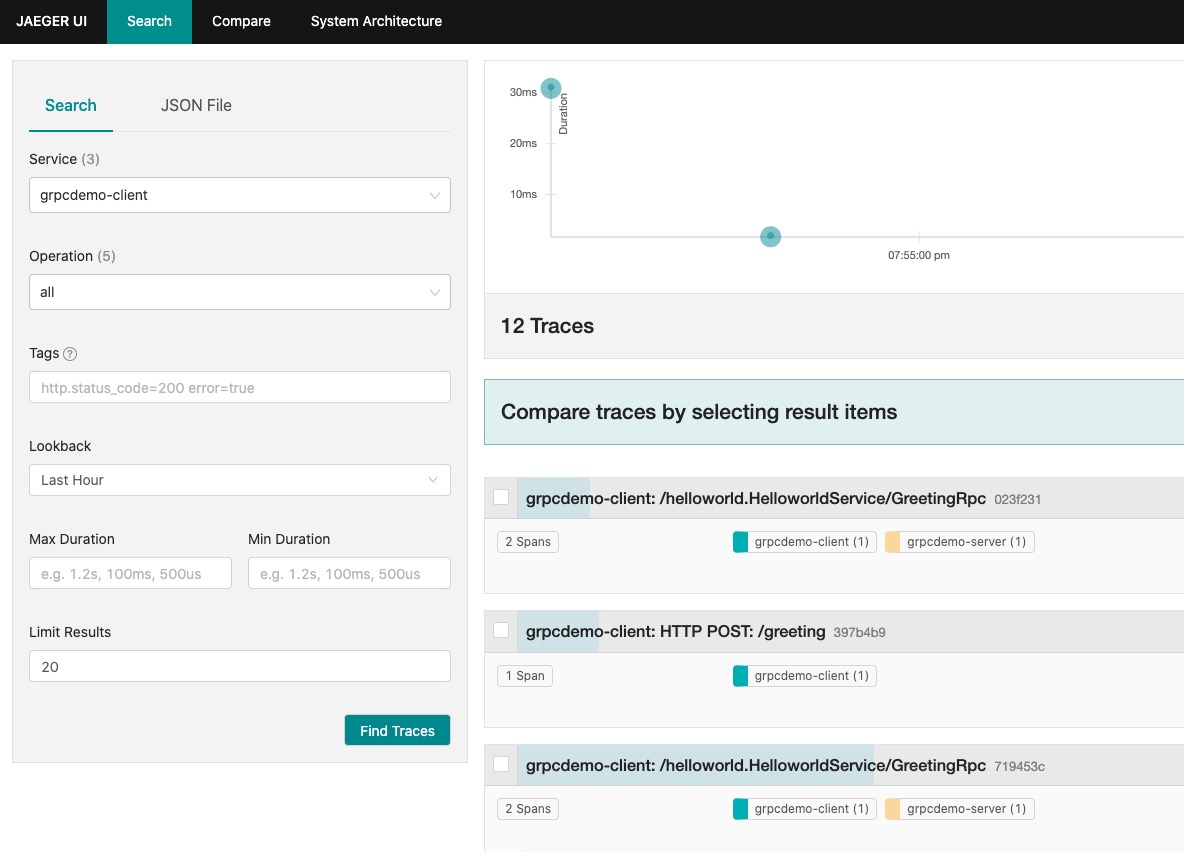
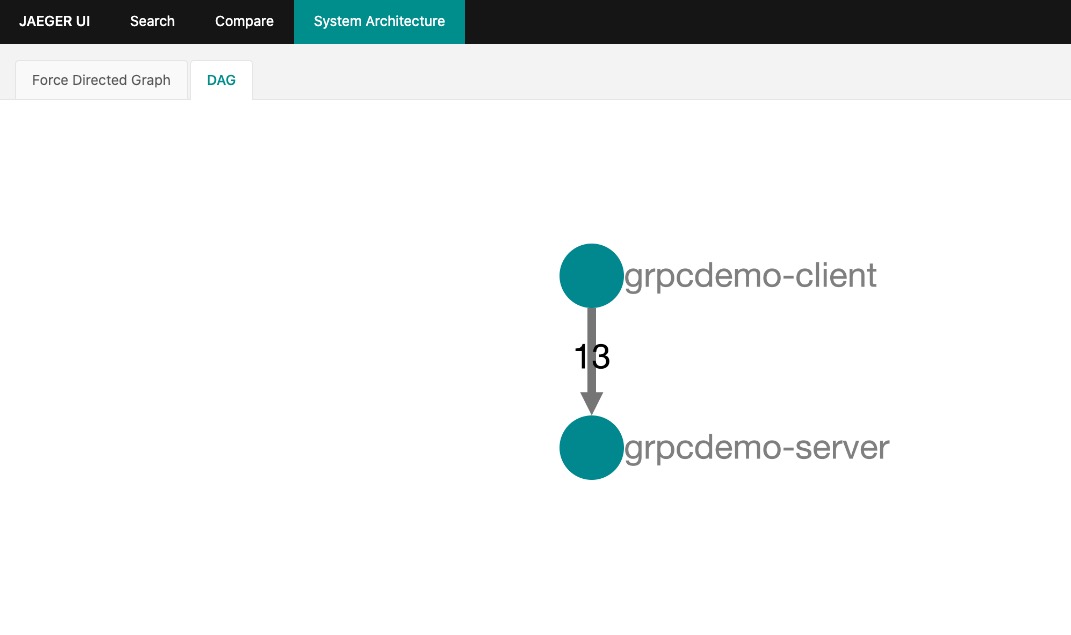
Screenshot
Jaeger Call Chain Monitoring
Usage
To integrate Jaeger call chain monitoring, follow these steps:
- Start Jaeger
docker run -d --name jaeger \
-p 6831:6831/udp \
-p 16686:16686 \
jaegertracing/all-in-one:1.29
2
3
4
- Add two lines of configuration to the
.envfile
JAEGER_AGENT_HOST=localhost
JAEGER_AGENT_PORT=6831
2
- Add three lines of code near the beginning of the
mainfunction
tracer, closer := tracing.Init()
defer closer.Close()
opentracing.SetGlobalTracer(tracer)
2
3
- On the server side, when calling the
grpcx.NewGrpcServerfunction to create agrpcx.GrpcServerinstance, add the opentracing interceptor with the two lines of codegrpc_opentracing.StreamServerInterceptor(),andgrpc_opentracing.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
func main() {
defer nacos.CloseNamingClient()
conf := config.LoadFromEnv()
tracer, closer := tracing.Init()
defer closer.Close()
opentracing.SetGlobalTracer(tracer)
svc := service.NewHelloworld(conf)
grpcServer := grpcx.NewGrpcServer(
grpc.StreamInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainStreamServer(
grpc_ctxtags.StreamServerInterceptor(),
grpc_opentracing.StreamServerInterceptor(),
grpc_prometheus.StreamServerInterceptor,
logging.StreamServerInterceptor(grpczerolog.InterceptorLogger(zlogger.Logger)),
grpc_recovery.StreamServerInterceptor(),
)),
grpc.UnaryInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainUnaryServer(
grpc_ctxtags.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
grpc_opentracing.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
grpc_prometheus.UnaryServerInterceptor,
logging.UnaryServerInterceptor(grpczerolog.InterceptorLogger(zlogger.Logger)),
grpc_recovery.UnaryServerInterceptor(),
)),
)
pb.RegisterHelloworldServiceServer(grpcServer, svc)
grpcServer.Run()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
- The client also needs to add the opentracing interceptor to the gRPC client connection instance, so that when the client initiates a gRPC request, the opentracing implementation (jaeger) can inject the span id into the metadata, otherwise the call chain with the server cannot be linked together.
func main() {
defer nacos.CloseNamingClient()
conf := config.LoadFromEnv()
tracer, closer := tracing.Init()
defer closer.Close()
opentracing.SetGlobalTracer(tracer)
tlsOption := grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials())
dialOptions := []grpc.DialOption{
tlsOption,
grpc.WithStreamInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainStreamClient(
grpc_opentracing.StreamClientInterceptor(),
)),
grpc.WithUnaryInterceptor(grpc_middleware.ChainUnaryClient(
grpc_opentracing.UnaryClientInterceptor(),
)),
}
grpcConn := nacos.NewWRRGrpcClientConn(nacos.NacosConfig{
ServiceName: "grpcdemo-server_grpc",
}, dialOptions...)
defer grpcConn.Close()
restProvider := nacos.NewWRRServiceProvider("grpcdemo-server_rest")
svc := service.NewEnumDemo(conf, pb.NewHelloworldServiceClient(grpcConn),
client.NewHelloworldClient(ddclient.WithClient(newClient()), ddclient.WithProvider(restProvider)))
handler := httpsrv.NewEnumDemoHandler(svc)
srv := rest.NewRestServer()
srv.AddRoute(httpsrv.Routes(handler)...)
srv.Run()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
Screenshots